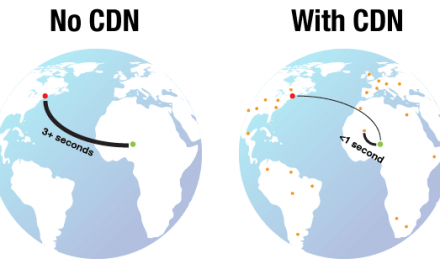
What is Anycast?
Usually, any device or server connected to the Internet will have a unique IP and the communication between them is one-to-one. This communication is known as Unicast where the data packets are sent from one point to another point.
Anycast, on the other hand, allows multiple servers on the network to use the same IP address/set of IP addresses. It advertises individual IP addresses on multiple nodes in the network. Communication with an anycast network is One-to-Nearest.
What is Anycast DNS?
In Anycast DNS, one IP address or set of IP addresses of the DNS servers is advertised on multiple nodes in the network. When a DNS request is made to a service using Anycast DNS, routers determine the closest DNS server by searching for the path with minimal network hops for the request to take. Selective routing makes the Anycast DNS network to be resilient against high traffic volume, network congestion, and Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks.
How Does Anycast DNS Function?
With Anycast a single destination address has multiple routing paths to two or more endpoint destinations. The DNS queries and responses will follow the shortest paths in order to answer queries as fast as possible. Anycast makes DNS resolving significantly faster depending on the number of PoPs which announce the DNS Anycast addresses. In addition, Anycast helps to keep DNS resolving services highly available.
Let’s Test the CDN Service With Unicast and With Anycast DNS
We have measured the latency with cURL. We have made HTTP requests from Seoul, South Korea to a png file with Content-Length: 204775, served by our CDN nodes in North America. First, a Unicast DNS server of ours located in the US has been responsible for resolving the domain name associated with the resource.
Then we migrated the DNS record for this domain on each of the Anycast DNS servers of ours strategically placed all around the world and made the same HTTP request to the same file. We measured the DNS Lookup time, TTFB, and the Total time of the requests.
Let’s compare and analyze the metrics we used to measure latency shown in the outputs:
| Metrics type: | Unicast DNS | Anycast DNS | Difference |
DNS Lookup |
1.714655 | 0.001520 | 1,713135 |
TTBF |
2.794355 | 0.708376 | 2,085979 |
Total |
3.374157 | 1.542313 | 1,831844 |
The time is measured in seconds.
As you may notice Anycast DNS reduces CDN service latency significantly. All this results in lowering the load time of your website’s resources and improving the experience of your visitors.
Universal CDN DNS upgrades. New Anycast PoP in Seoul, South Korea
We are happy to announce that Universal CDN Anycast DNS network has been extended with a new location – Seoul, South Korea. Now, along with our Anycast PoPs in Sao Paulo, Johannesburg, South Africa, Singapore, Tokyo, and many others, this update in our network infrastructure enhanced the acceleration in the CDN domain resolution now and for visitors from East Asia.
With these new locations, our Universal CDN Аnycast DNS network now spans six continents. All Anycast DNS PoPs are enabled for our clients at no additional costs.
Summary
Universal CDN uses Anycast DNS to enhance DNS availability and DDoS attacks mitigation, to lower CDN service latency by speeding up the DNS resolution and the delivery of TTFB, and last but not least to improve CDN service reliability.
If not registered, we provide fast, reliable, and feature-rich Content Delivery Network services, as well as an intuitive, easy-to-use Control Panel.
Get a FREE Welcome Bonus to test our services.
Sign Up for a FREE CDN START